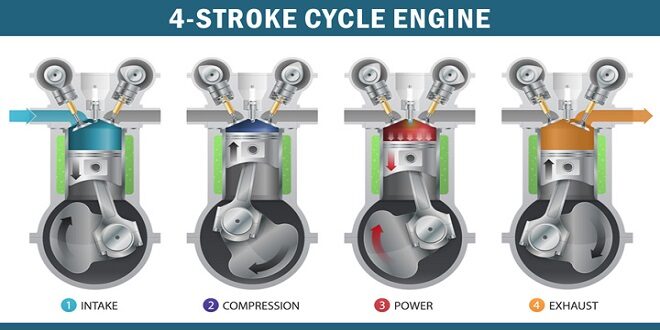
The purpose of this technical paper is to inform the reader about the modern automobile four-stroke engine. To accomplish this, we have assumed that the reader has an elementary knowledge of the mechanics of an engine which is gained by knowledge in the areas of solid mechanics, thermodynamics, fluids, dynamics, vibrations, machine elements, manufacturing, calculus, and physics.
Preface
Perhaps the most well-known engine type in the world, the automotive four-stroke engine has become the power plant of choice for today’s consumers due to its greater efficiency and cost-effectiveness over alternate reciprocating engines.
Perhaps the most well-known engine type in the world, the automotive four-stroke engine has become the power plant of choice for today’s consumers due to its greater efficiency and cost-effectiveness over alternate reciprocating engines.
came in 1862 when a French engineer, Alphonse Beau de Rochas, designed and patented the first four-stroke engine. In 1864 an Austrian engineer, Siegfried Marcus, build the first gasoline-powered vehicle, which was comprised of a cart and a one-cylinder engine. But the biggest breakthrough came in 1876 when Nikolaus August Otto invented the first successful four-stroke engine, aptly nick-naming 13 the four-stroke cycle the ”Otto Cycle.
History of the Four-Stroke Automobile Engine
The next great milestone in the development of the four-stroke engine was achieved by Gottlieb Daimler in 1885, who invented an engine with a vertically positioned cylinder, fueled by gasoline injected into a cylinder chamber through a carburetor.
The innovations from these important inventors over the years culminated in Daimler’s engine which is commonly referred to as the ” blueprint” to the modern-day internal combustion engine.
From the inception of the four-stroke internal combustion engine, many paths have been explored and followed to create a superior design, especially in the configuration of the cylinders. In general, there are seven types of reciprocating engine designs, an engine that employs one or more cylinders in which a piston(s) reciprocates back and forth. The first of these designs was the single-cylinder engine.
After its success, designers began to play with twin engines, or two-cylinder engines which lead to the In-Line Engine, the V Engine, the Opposed Cylinder Engine, the W engine, the Opposed Piston Engine, and the Radial Engine. These different setups were further explored with engines such as the Vauxhall Wyvern and Velox engines to the Ford V-Four engine, utilizing an even greater number of cylinders than the original twin-engine
Today’s four-stroke engine manufacturer mainly builds In-Line or V-configured engines. Perhaps the most widely recognized engine today is the Chevrolet Small Block V8 Engine. This engine was made popular through its dependability and through hobbyists and the performance market because of the interchangeability of parts. After 35 years, General Motors discontinued its infamous engine, replacing it with the new Generation II engine in 1992.
Last word
seemingly has dominated today’s after-market industry, other manufacturers have successfully made engines for their vehicles from the Ford V-eight to the Cadillac North Star, to the Porsche In-Line Six as well as mainly others.